Cat Health

Cat health starts with everyday care. It’s more than just going to the vet once a year. From nutrition and grooming to vaccines and checkups, small habits make a big difference. Every life stage—kitten, adult, or senior—has its own set of needs.
Our articles cover common concerns like upset stomachs, weight issues, itchy skin, and dental health. You’ll also find guidance on how to recognize symptoms early and when to call the vet. If you’re curious about diet, hairballs, allergies, or behavior changes, you’re in the right place.
Explore simple wellness tips and easy home routines that help your cat stay comfortable, active, and happy. A little knowledge can lead to fewer emergencies, healthier habits, and more peace of mind for you and your pet.

Heart Disease in Cats: Warning Signs, Vet Tips & What You Can Do
Let me tell you something I wish I had known years ago: cats are masters of disguise. Especially when it ...

Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV)- Protect Your Cat Now
Certainly one of the most devastating diseases affecting cat populations around the world is feline leukemia. The feline leukemia virus ...

What is Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV)?
Until the late 1980s, the feline leukemia virus was the only agent linked to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in cats—that is, ...

The Itchy Cat
Many disease conditions can produce itching in cats. However, only a few disorders result in severe and/or prolonged itching. The ...
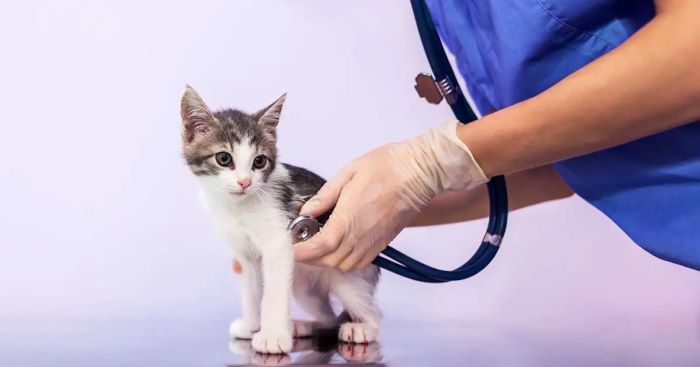
Cat’s First Vet Check-up
For the best possible start, take your new cat to a vet as soon as you can for a comprehensive ...
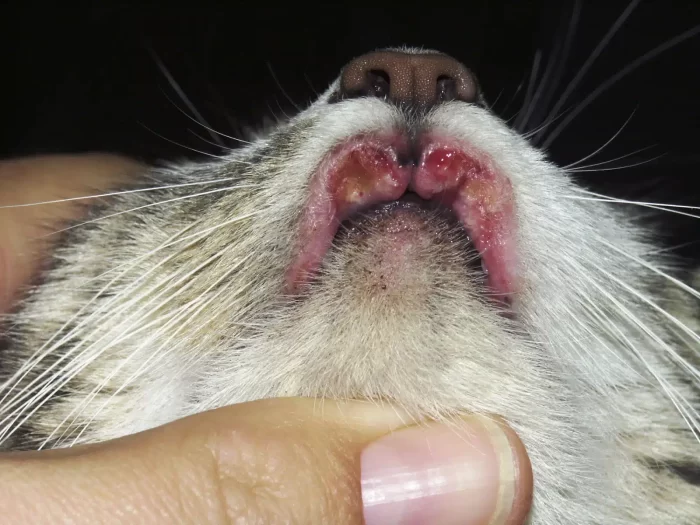
Cat’s Eosinophilic Granuloma Complex
This dermatopathy of cats is characterized by the unexplained appearance of red to yellow-brown ulcerated lesions with associated hair loss ...
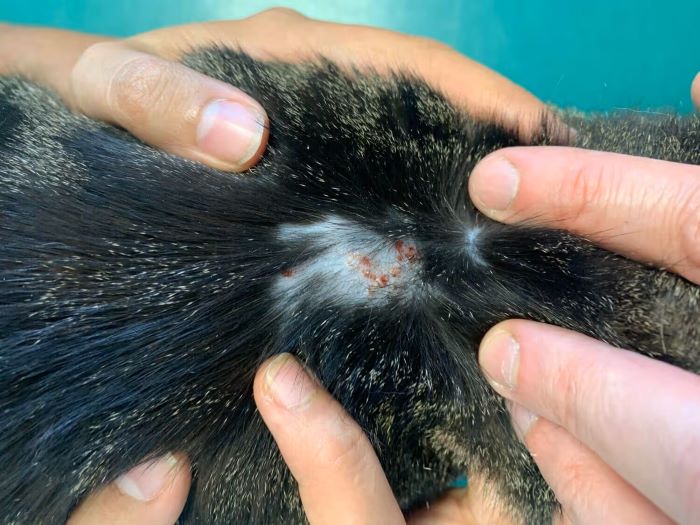
Cat’s Miliary Dermatitis
Miliary dermatitisrefers to a specific way in which feline skin responds to inflammation and/or irritation. Such a skin reaction is ...
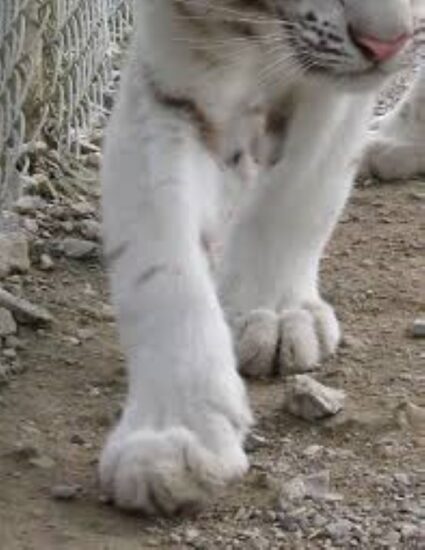

Metabolic Bone Disease
Metabolic bone diseases are characterized by a thinning and loss of bony mass, predisposing the bone to fractures and growth ...
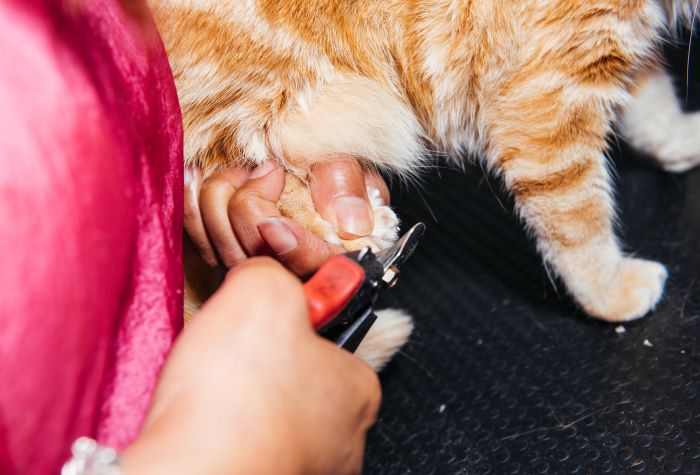

Declawing Cats
The decision as to whether to have a cat declawed is certainly a controversial one, yet it is one that ...

Diabetes Insipidus in Cats
This type of diabetes should not be confused with diabetes mellitus, which involves abnormal glucose metabolism. Diabetes insipidus involves abnormal ...
